
- April 17, 2024
- 0 comments
- 245 Views

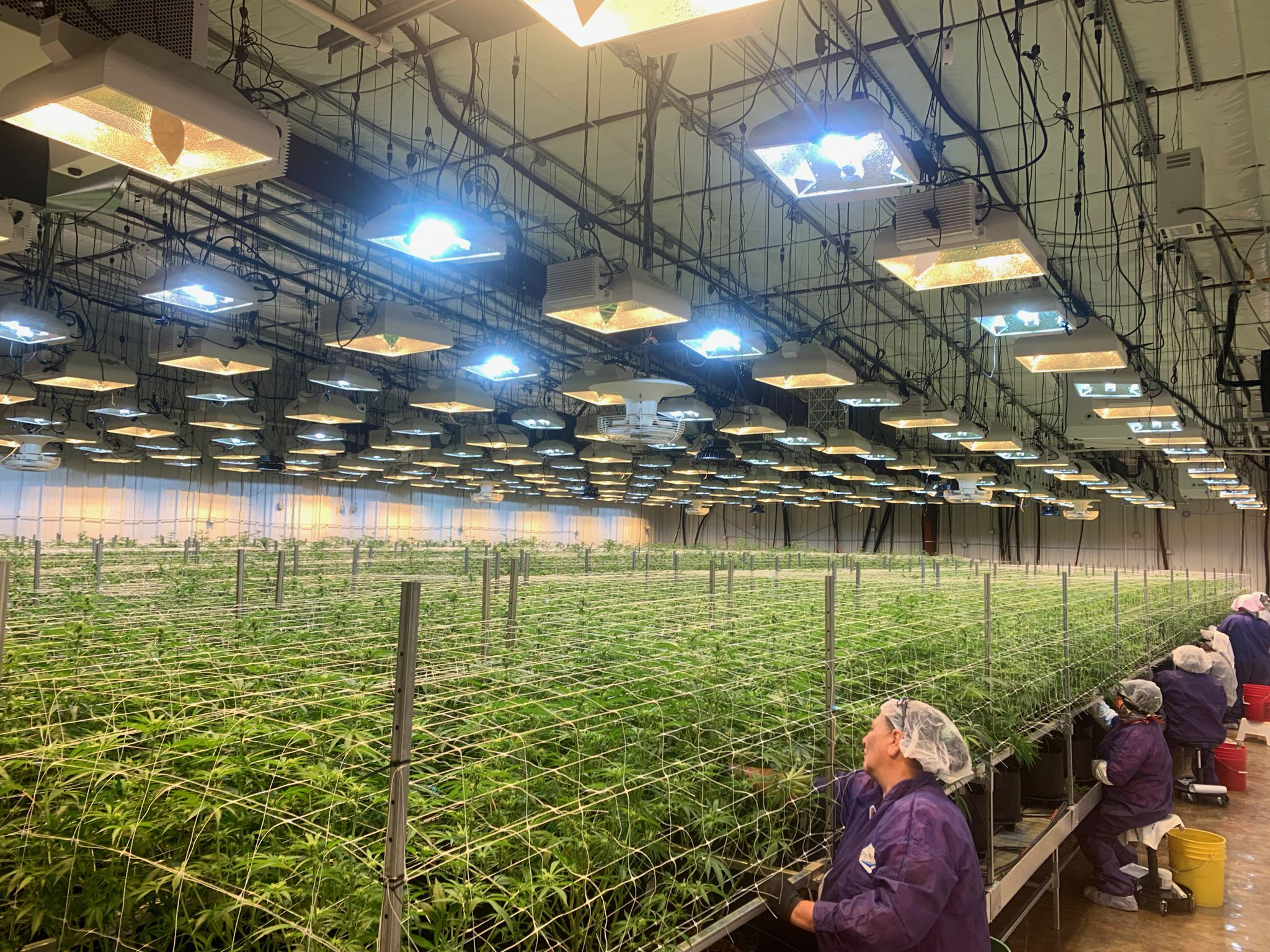
Growers need a lot of different equipment to foster the ideal conditions for cultivating high-yield, high-quality cannabis indoors. We’ll walk you through your options, depending on your preferred cultivation method, operational size and budget, starting with the crucial decision of whether to use a grow tent or a grow room.
Grow tents versus grow rooms
Unless you’re a greenhouse grower, your first decision is whether to use a grow tent or construct a grow room from scratch.
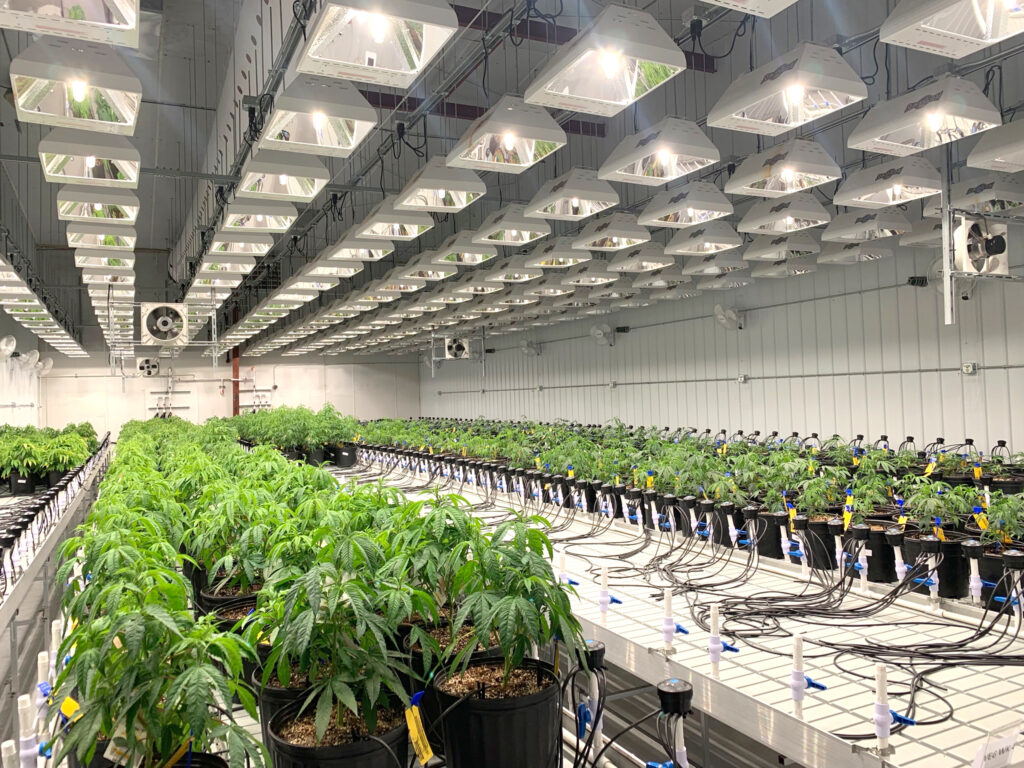
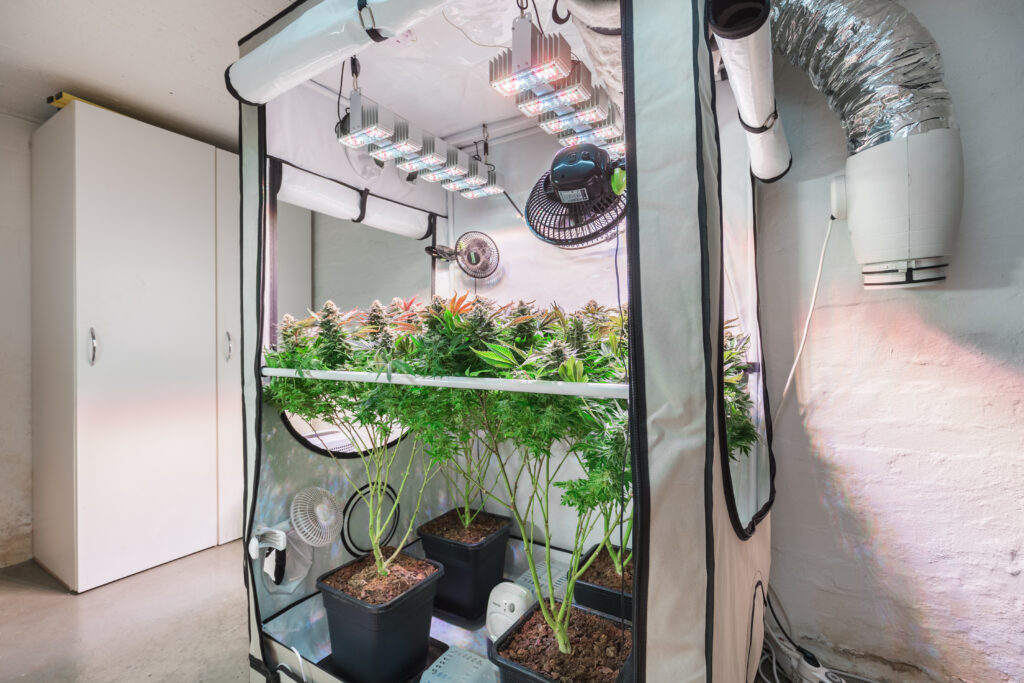
A grow tent provides cannabis with an ideal indoor environment without occupying an entire room. They vary in size, making them ideal for hobbyist farmers who just want to grow a couple of plants. They’re also suitable for smaller commercial operations.
Grow tents not only make it easier to install lighting and ventilation, but they also capture maximum light for photosynthesis. That’s because their interiors are covered with reflective material. Imagine a flashlight shining into the darkness.

The light beam fans out, dispersing into a cone shape. So, although the central light from the bulb reaches the plants effectively, all of that peripheral light remains underutilized. By incorporating reflective material like mylar, aluminum foil, panda film or orca film, the grow tent redirects all light to the plants.
Grow rooms, by contrast, are just as their name implies: entire rooms or enclosed areas dedicated to plant cultivation. Because they are custom built by the grower, they allow for greater flexibility in terms of both design and space.
Cultivation equipment
Regardless of whether you opt for a grow tent or a grow room, your setup still requires several pieces of equipment to create a controlled growing environment. We’ve compiled a comprehensive list.
Lighting
Light is the most critical environmental factor for growing cannabis. It is, of course, a plant’s energy source. Moreover, if you’re growing a photoperiod variety, light triggers flowering and other developmental changes in the plant. Both the amount and type of light are essential.
Many artificial light sources can be used (see the table below). While HID bulbs were once the most popular because of their high light intensity, high-quality LEDs are now available that provide the full spectrum of light that cannabis needs at about half the energy cost.

Table: Spectral output and lifespan by artificial light type
Lamp type
Spectral output
Life span (hrs)
Incandescent
Broad spectrum
1,000
Fluorescent
Broad spectrum
1,000 – 30,000
HPM
Broad spectrum
10,000 – 20,000
HPS
Broad spectrum
10,000 – 30,000
Metal halide
Broad spectrum
10,000 – 20,000
LED
Specific wavelength
> 50,000
Plasma
Full spectrum
30,000 – 50,000
Induction light
Narrow, adjustable
50,000 – 100,000

Ventilation
Proper airflow is crucial for maintaining the optimal climate in the grow tent or grow room, and a ventilation system allows for continuous airflow between the outdoors and the indoor grow area. Most grow-room ventilation systems use a combination of fans and ducts. There are numerous pieces of equipment that growers can integrate into a ventilation system:
- Exhaust fans remove hot, humid air from the grow area.
- Intake vents work in tandem with exhaust fans to allow cool, fresh air inside.
- Ducts are required when using exhaust fans and intake vents to direct airflow. The ductwork must be adequately insulated and sealed to prevent energy loss and ensure unobstructed air circulation.
- Louvers and dampers serve as regulators, giving growers precise control over the volume of air entering and leaving the grow area.
- Heaters and air conditioners heat or cool the growing area, ensuring a stable, consistent desired temperature.
- Dehumidifiers help keep the relative humidity in the ideal range of 40‒70%.
- Oscillating fans keep a nice, gentle breeze inside the grow area, blowing air constantly around the plants to ensure uniform air dispersion. Your average pedestal fan works fine.
- Fan controllers are used to modulate fan speeds to the specific needs of the plant variety, simulating natural wind-flow changes.
- Carbon filters, also called carbon scrubbers, neutralize odors, preventing their spread outside the grow area.
Growers that have large-scale operations or prefer precise control over the environment should invest in a comprehensive HVAC (heating, ventilation and cooling) system.
Climate control: temperature, humidity and pH
Having a good ventilation system is necessary for creating the ideal climate for cannabis, but growers also need the right measurement tools to monitor and control the environment.[1] This includes measuring the pH of the nutrient solution, which is critical for ensuring that all essential nutrients are available to the plant for uptake:
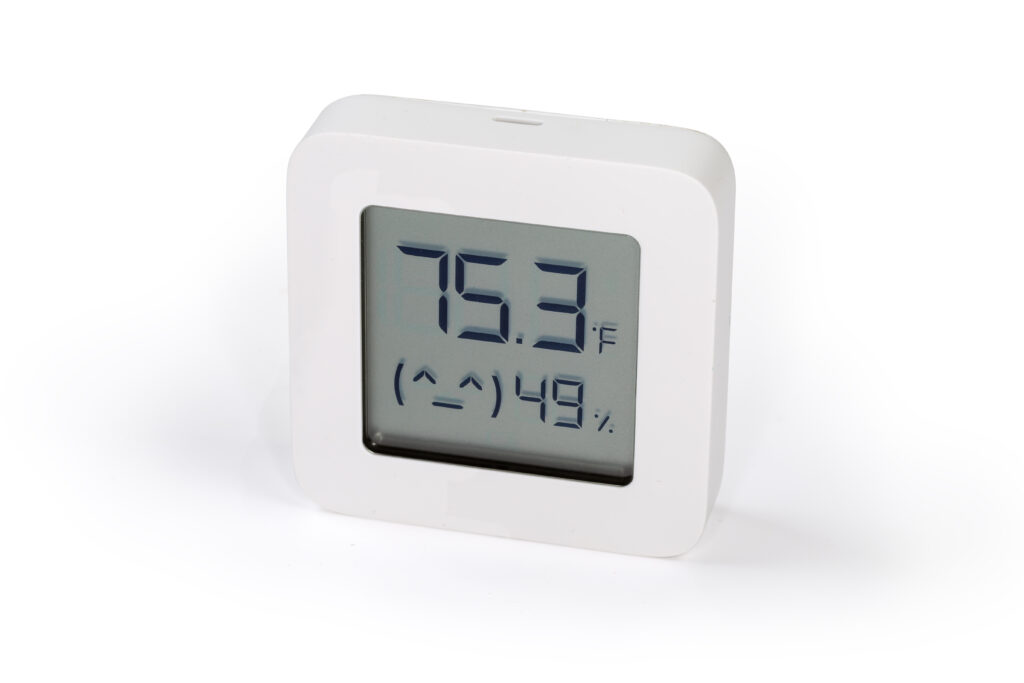

- Thermostats monitor the temperature of the grow area. If connected to an HVAC system, they can automatically keep the temperature at a certain degree or within a specific range. Cannabis flourishes in temperatures ranging from 65 to 80°F.
- Hygrometers measure real-time temperature and humidity. For the most accurate reading, place them in the middle of the grow area away from direct contact with plants or heat sources. Humidity levels should be maintained in the 40‒70% range.
- pH meters measure the acidity or alkalinity of a nutrient solution. The ideal range for hydroponically grown cannabis is pH 5.5‒6.5.
- TDS or EC meters check water quality. TDS, which stands for total dissolved solids, is measured in parts per million (PPM). EC, which stands for electrical conductivity and reflects the ability of a nutrient solution to conduct electricity, is measured in millisiemens per centimeter (mS/cm).
[1] Maintaining the right temperature and humidity levels is crucial for achieving a balanced vapor pressure deficit (VPD), which helps plants take up water and nutrients.
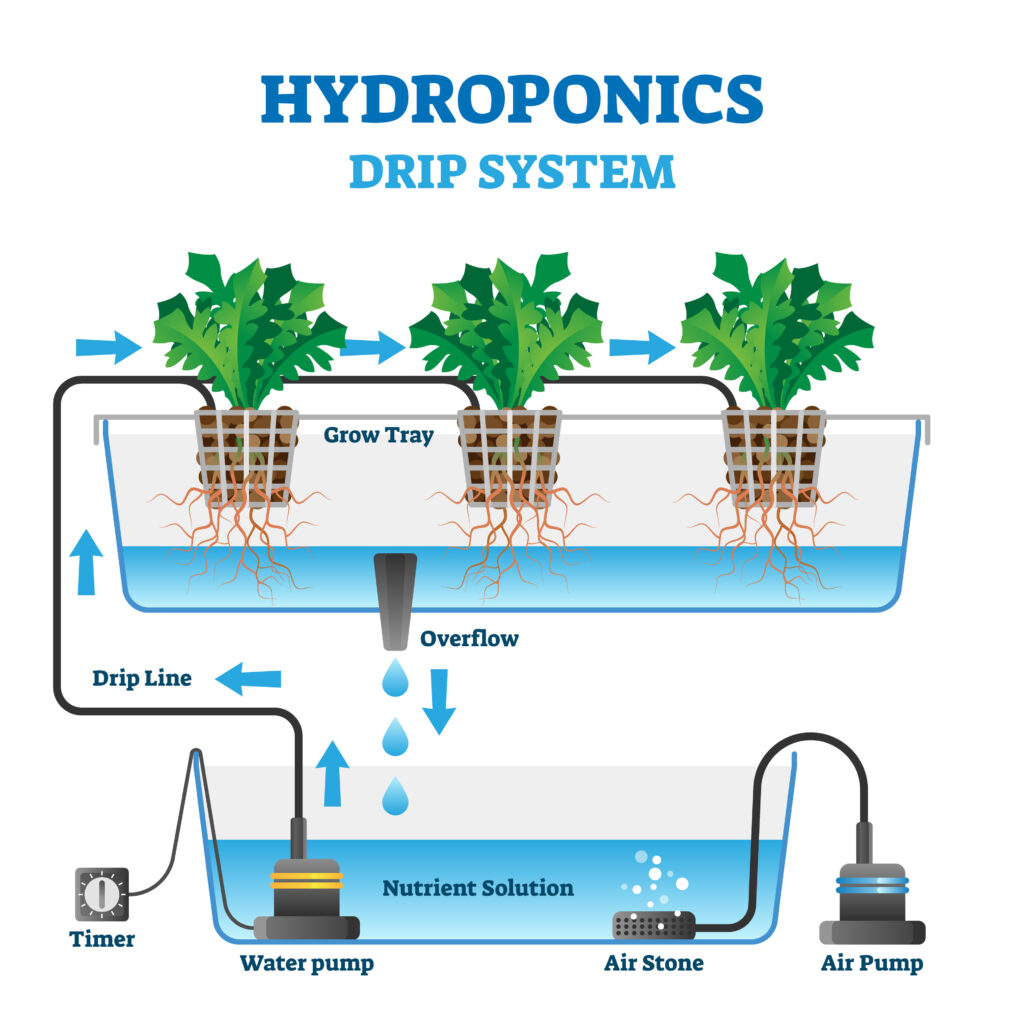
Irrigation
An irrigation system is needed to provide plants with water and nutrients. Investing in high-quality irrigation equipment, such as a drip system or misters, ensures precise, efficient water and nutrient delivery, reduces waste, and safeguards against moisture-related diseases.
An automated irrigation system typically includes a large reservoir stationed outside of the grow area, with a water pump set to a timer:
- Water reservoirs store water. Growers can use a barrel, a bucket or even a tub—whatever can hold enough water to irrigate the crop.
- Water pumps pull water into the irrigation system. They need just enough power and pressure to ensure that water and nutrients are equally distributed to all the plants.
- Digital timers turn off the water supply at regular intervals.
- Oxygenators keep the water or nutrient solution in the reservoir oxygenated, helping prevent harmful bacteria or fungi from growing and oxygenating the growing medium or substrate. If the reservoir is no larger than 120 liters, regular air pumps or air stones are sufficient to oxygenate the water or nutrient solution. With larger reservoirs, you can use a stirring pump. Ozone generators are also used in large-scale operations.
- Drip rings or individual drippers of a sprinkler system irrigate the plants.

Growing medium
If a grower is cultivating cannabis indoors, they need to choose an appropriate growing medium. An effective growing medium has a physical structure capable of maintaining a good balance between air and water retention during irrigation and between feedings to prevent root asphyxia and drought stress. The growing medium also needs to provide a suitable biological and chemical environment for plant roots to access nutrients.
Commonly used growing mediums include the following:
- Coir-based: pure coir (loose), coir, and perlite (loose)
- Rockwool
- Phenolic foam
- Peat-based
- Living soils
Carbon dioxide generators
Carbon dioxide tanks and regulators provide additional carbon dioxide to grow areas, which helps promote photosynthesis and plant growth.
Processing equipment
When the cannabis is ready for harvest, growers need tools to collect and process the buds, including:
- Trimming machines, which physically remove the buds from the plant. They can be as simple as gardening hand trimmers or as sophisticated as machine trimmers. Air tumblers and gravity-fed devices are also options.
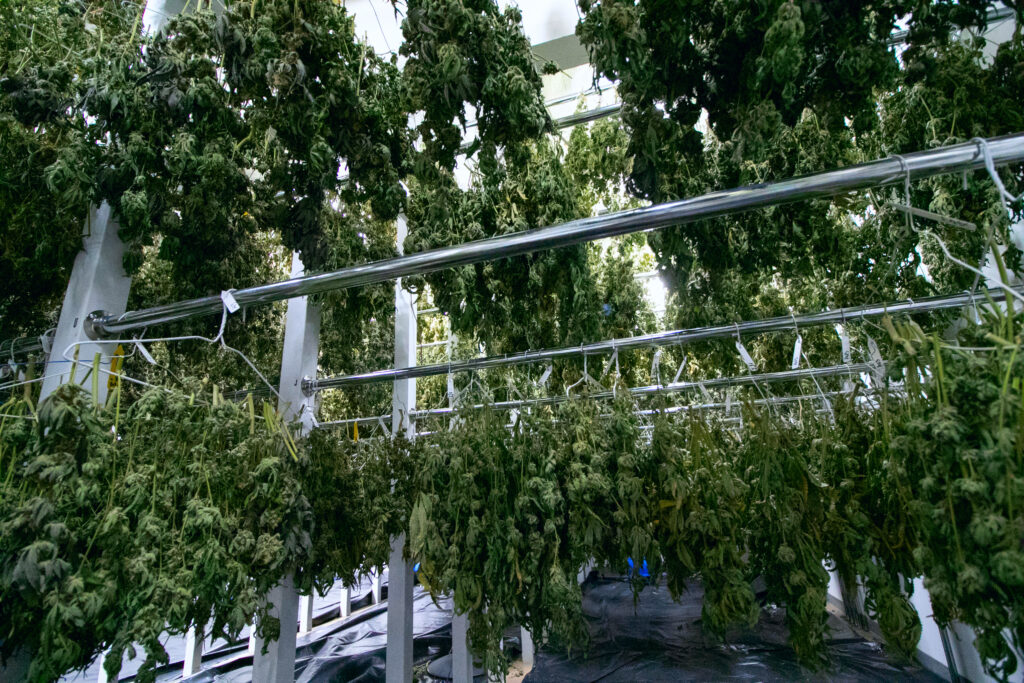
- Drying racks expedite moisture extraction from cannabis harvests, can help maximize yield and ensure the cannabis is properly cured. They’re typically a frame with multiple levels of mesh screens or trays. Growers spread the buds out on them, allowing air to circulate freely and evenly. Growers need to ensure proper air circulation during the drying process to prevent mold, mildew or inconsistent drying.
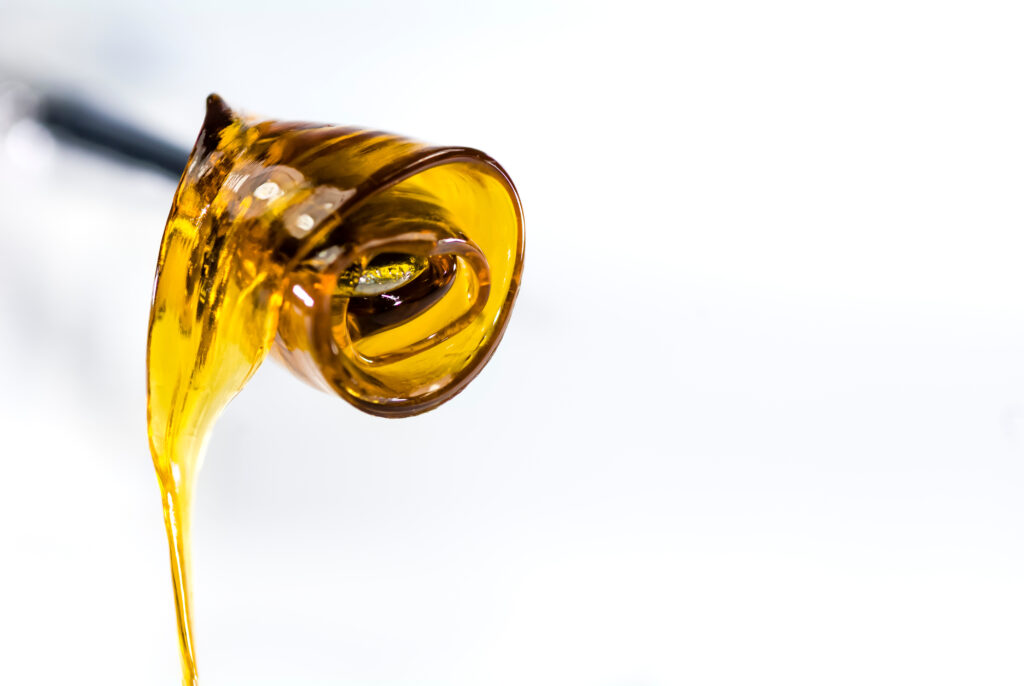


- Extracting equipment is used to extract cannabinoids and terpenes from the plant material. Growers should carefully select their extraction equipment to ensure it aligns with their goals and helps them optimize the extraction process. There are three types of extraction equipment:
- Solvent-based extraction uses solvents such as butane, propane or other hydrocarbons to extract cannabinoids and terpenes. The equipment typically consists of extraction vessels, solvent tanks, pumps and recovery systems to extract and recover the solvent safely and efficiently.
- Solventless extraction facilitates mechanical separation by means of a rosin press or ice water hash, while preserving crop quality and facilitating maximum yields.
- Supercritical carbon-dioxide extraction uses carbon dioxide at an elevated pressure and temperature. With this method, carbon dioxide becomes a supercritical fluid, allowing it to solubilize non-polar compounds. Look for equipment that precisely controls temperature, pressure and CO2 flow rates to optimize the extraction parameters and achieve the desired yields and purity.[1]
- Packaging machinery. Growers will usually need to purchase machinery that is customized to their exact specifications, such as weight, vertical space availability, bag size and speed of delivery.
Security and surveillance equipment
Growers might also want to invest in security and surveillance equipment, as it provides extra protection—and, depending on local legislation, keeps grow operations in compliance with laws and regulations. Some security and surveillance equipment they should consider include:
- Security cameras. Strategically place high-resolution cameras throughout the facility to monitor it inside and out. Consider placing them in ways that enable you to fully monitor the grow and processing areas, entrances, exits and perimeter fences.
- Alarm and access control system. The use of intrusion alarms, panic buttons and duress alarms connected to a central monitoring station alert authorities or a security team in case of unauthorized access, break-ins or emergencies.
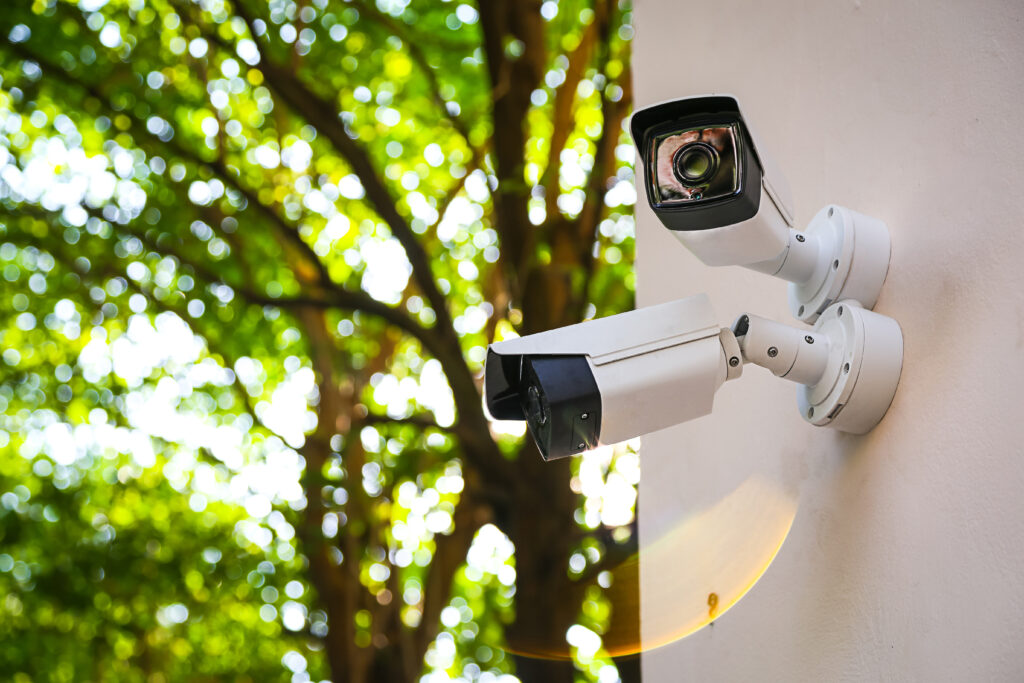

Surveillance equipment doesn’t just apply to security, however. Growers can also install automated sensors and monitoring software to care for their crops even when nobody is on the premises. Using both allows growers to monitor and control the temperature, humidity, carbon-dioxide levels and other environmental factors critical to plant health automatically, thus enabling growers to establish the perfect indoor growing environment for their cannabis with little manual work.
The Emerald Harvest Team